How To Use FD Rapid GolgiStain
Using the FD Rapid GolgiStain is a complex and delicate procedure that requires careful handling and attention to detail. Here's a general overview of the steps involved in using the FD Rapid GolgiStain:
Materials Needed:
- FD Rapid GolgiStain kit (commercially available).
2. Brain tissue samples (usually from small animals like rats or mice).
Procedure:
- Sacrifice the animal and extract the brain immediately.
- Slice the brain tissue into thin sections (100-200 micrometers thick) using a vibratome or a microtome.
1. Tissue Preparation:

- Place the brain sections into the impregnation solution from the FD Rapid GolgiStain kit. This solution contains silver nitrate and potassium chromate.
- The impregnation process typically lasts for 1 to 2 weeks, during which the silver chromate reaction product forms within a small subset of neurons.
2. Impregnation:
- After the impregnation period, carefully remove the brain sections from the impregnation solution.
- Dehydrate the sections in a series of increasing alcohol concentrations (e.g., 50%, 75%, 95%, 100% ethanol).
- Transfer the dehydrated sections to a clearing agent (e.g., xylene) to make them transparent.
- Mount the cleared sections onto glass slides using a mounting medium.

3. Dehydration and Mounting:
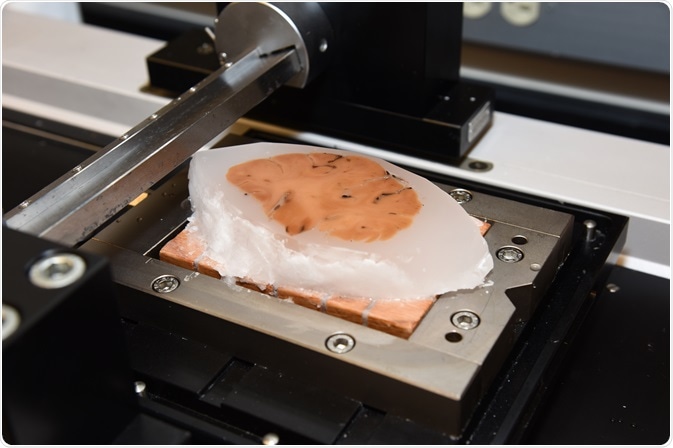
- Once the slides are ready, use a microtome to cut very thin sections (usually around 30-60 micrometers thick).
- Float the sections on a warm water bath (around 45-50°C) and pick them up onto gelatin-coated slides.

4. Sectioning and Staining:
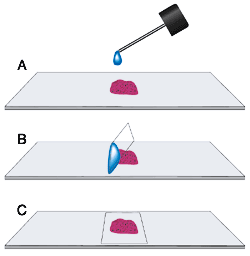
- Let the sections dry completely on the slides.
- Apply a coverslip using a suitable mounting medium.
5. Coverslipping:
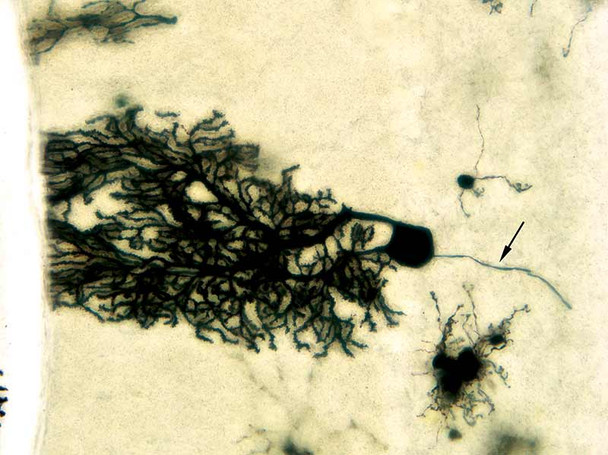
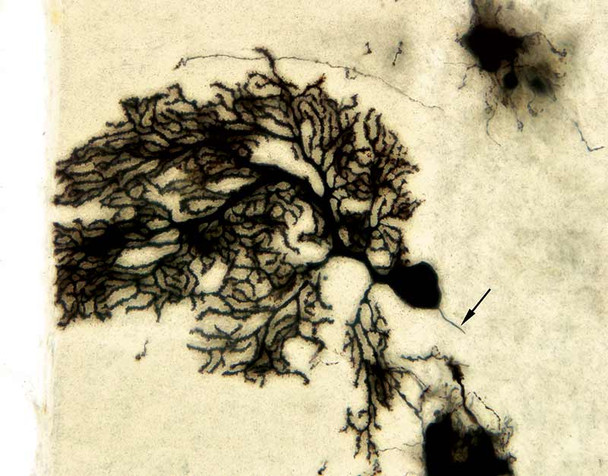
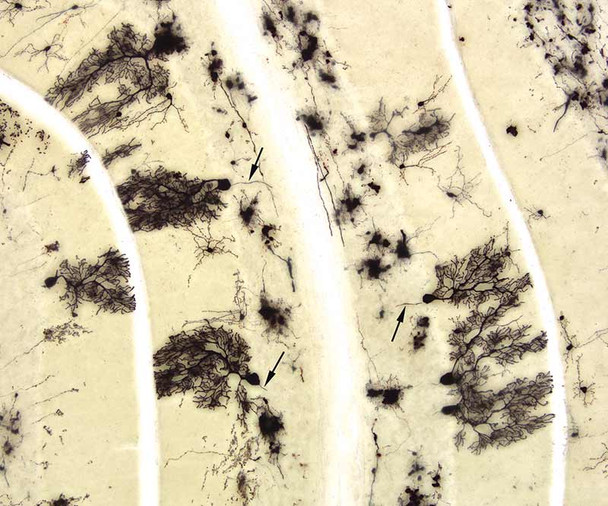
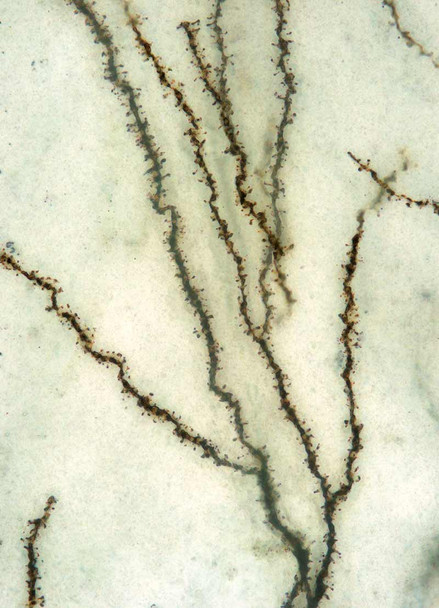
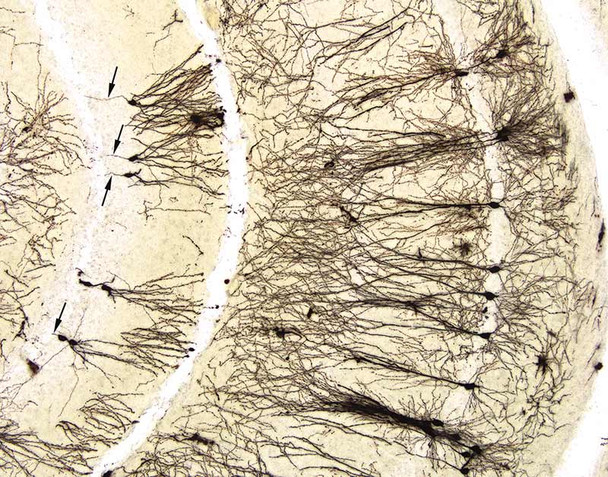
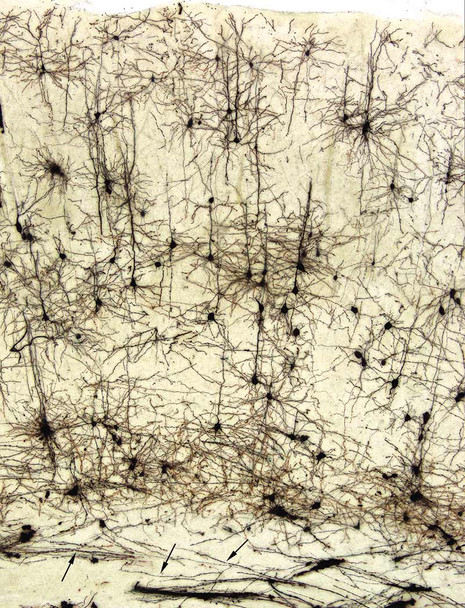
- Examine the slides under a microscope with appropriate magnification to visualize the stained neurons and their structures.
- Record and document the morphology of the labeled neurons using image capture systems.
6. Microscopic Analysis:
- Examine the slides under a microscope with appropriate magnification to visualize the stained neurons and their structures.
- Record and document the morphology of the labeled neurons using image capture systems.